Pandas & Reading Data
To make reading files easier, we will use the Pandas library that lets you read in structured data files very efficiently. Pandas, Python Data Analysis Library, is an elegant, open-source package for extracting, manipulating, and analyzing data, especially those stored in 2D arrays (like spreadsheets). It incorporates most of the Python constructs and libraries that we have seen thus far.
(Pandas is installed on all the lab machines. If you are using your own machine, see the directions at the end of Lab 1 for installing packages for Python.)
In Pandas, the basic structure is a DataFrame which stored data in rectangular grids. Let's use this to visualize the change in New York City's population. First, start your file with an import statements for pyplot and pandas:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pdWe used matplotlib in the Lab 3 and Lab 4 for plotting. The as plt allows us to use the plotting commands without having to write matplotlib.pyplot everytime, instead we just write plt. Similarly, The as pd allows us to use pandas commands without writing out pandas everytime-- we just write pd.
Next, save the NYC historical population data to the same directory as your program. This is a "comma separated values" file-- which is a plain text file containging spreadsheet data, with commas separating the different columns (thus, the name). Here's the first 10 lines of the file:
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demographics_of_New_York_City,,,,,, * All population figures are consistent with present-day boundaries.,,,,,, First census after the consolidation of the five boroughs,,,,,, ,,,,,, ,,,,,, Year,Manhattan,Brooklyn,Queens,Bronx,Staten Island,Total 1698,4937,2017,,,727,7681 1771,21863,3623,,,2847,28423 1790,33131,4549,6159,1781,3827,49447 1800,60515,5740,6642,1755,4563,79215Note that it has 5 extra lines at the top before the column names occur. The pandas function for reading in CSV files is read_csv(). It has an option to skip rows which we will use here:
pop = pd.read_csv('nycHistPop.csv',skiprows=5)
Before going on, let's print out the variable pop. pop is a dataframe, described in the reading above:
print(pop)The last line of our first pandas program is:
pop.plot(x="Year")which makes a graphical display of all of the data series in the variable pop with the series corresponding to the column "Year" as the x-axis. Your output should look something like:
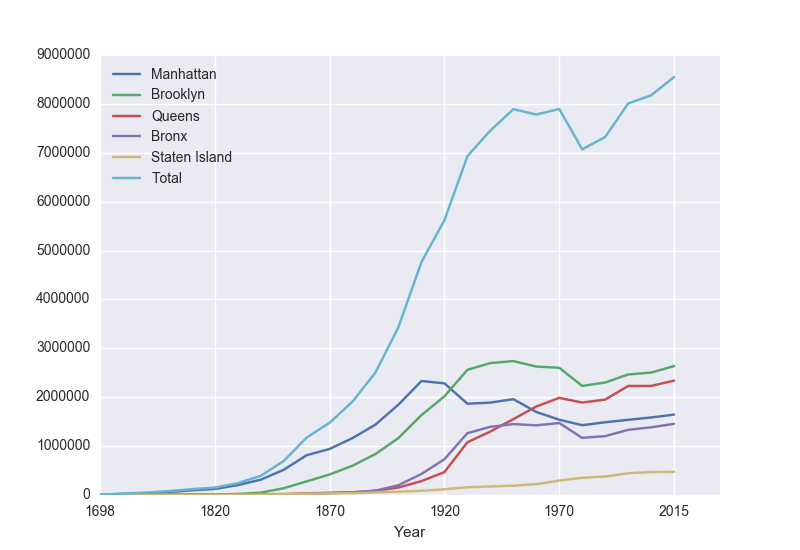
To recap: our program is:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
pop = pd.read_csv('nycHistPop.csv',skiprows=5)
pop.plot(x="Year")
plt.show()
which did the following:
- Imported the pandas library that contains structures and functions for organizing and visualizing data. We also imported the pyplot library which pandas uses to create figures.
- It read in a CSV file, containing NYC population historical data.
- It displayed the data as a visual plot of years versus borough populations.
- The last line shows the figure you created in a separate graphics window.
print("The largest number living in the Bronx is", pop["Bronx"].max())
Similarly the average (mean) population for Queens can be computed:
print("The average number living in the Queens is", pop["Queens"].mean())
Challenges
- What happens if you leave off the x = "Year"? Why?
- What happens if you add in x = "Year", y = "Bronx"?
- What does the series functions: .min(), .std(), and .count() do?