Submit the following programs via Blackboard:
- Due Date: 5 February Reading: Chapters 1 & 2
Write a program that prints your name to the screen 20 times. - Due Date: 9 February Reading: Chapters 1 & 2
Choose a (printable) character from the keyboard. Write a program that prints an opening statement and then asks the user for a number and prints your character that many times.For example:
The fault is in our stars... Please enter a number: 2 * *
Another sample run:
The fault is in our stars... Please enter a number: 5 * * * * *
Note: your program should have a statement you like (different from the sample and unique to you, so that the cheat-checking program does not flag it as someone's work) and print a character you choose (again, different from the character chosen above).
- Due Date: 10 February Reading: Chapter 2
Write a program that implements the pseudocode ("informal high-level description of the operating principle of a computer program or other algorithm") below:1. Ask the user for the size of their apartment in square meters (size) 2. Convert the size to square feet using the formula: convertedSize = size * 10.764 3. Print out the converted size.
- Due Date: 11 February Reading: Chapter 2
Write a program that asks the user for the diameter of a circular table and prints out the circumference. For example, if the user enters 10, your program should print out 31.4159265359.
Hint: The circumference of a circle is Pi*d where d is the diameter of the circle. - Due Date: 13 February Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that will print out a conversion table for dollars and another currency. The currency you should use is based on the first letter of your first name:
For example, if your first name is Eric, you would use Euros. From the table above, we have that one dollar is worth 0.77 euros. You should begin the program by printing out your name. On each line, your program should write the number of dollars and the corresponding number of your currency. For example:If your name begins with... Use the currency: $1 is worth: A Afghan Afghani (AFN) 51.08 B Bangladeshi Taka (BDT) 80.58 C Costa Rican Colon (CRC) 499.38 D Danish Krone (DKK) 5.67 E Euro (EUR) 0.77 F Falkland Island Pound (FKP) 0.62 G Guatemalan Quetzal (GTQ) 0.13 H Hungarian Forint (HUF) 0.00456 I Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) 9639.99 J Japanese Yen (JPY) 83.85 K Kenyan Shilling (KES) 0.0116 L Lebanese Pound (LPP) 0.000664 M Moroccan Dirham (MAD) 0.118 N Nepalese Rupee (NPR) 0.0115 O Omani Rial (OMR) 0.384 P Polish Zloty 3.11 Q Qatari Riyal (QAR) 0.275 R Russian Ruble (RUB) 30.80 S Somali Shilling (SOS) 0.000619 T Thai Baht (THB) 30.59 U Ukrainian Hryvna (UAH) 8.10 V Venezuelan Bolivar (VEH) 4.30 W Samoan Tala (WST) 2.27 X East Caribbean Dollar (XCD) 2.70 Y Yemeni Rial (YER) 0.00477 Z Zimbabwean Dollar (ZWD) 361.90 Eric's converting program Dollars: Euros: 1 0.77 2 1.53 3 2.3 4 3.07 5 3.84
Your program should print the information for 1, 2, ..., 5 dollars. You do not need to worry about formatting (we will talk about that more in Chapter 5), but you do need to calculate all 5 entries.
Hint: modify the second program from the Lab 2.
- Due Date: 18 February Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that implements the pseudocode below:1. Ask the user for the number of days until finals. 2. Print out the weeks until finals (weeks = days // 7) 3. Print out the leftover days (leftover = days % 7)
- Due Date: 19 February Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that asks the user for time in days and prints the number of years and days (assume that there are 365 days in a year). For example, if the user entered, 1000, your program would output, 2 years 270 days. Note that you should use "years" and "days" for all inputs (even in the cases where it is grammatically incorrect). - Due Date: 20 February Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that asks the user for 10 numbers and prints out the total.Here is a sample run of the program:
Please enter a number: 5 Please enter a number: 2015 Please enter a number: -100 Please enter a number: 3 Please enter a number: -999 Please enter a number: 8 Please enter a number: 67 Please enter a number: 19 Please enter a number: 17 Please enter a number: -1234 The total is -199
- Due Date: 23 February Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that asks the user for 15 letters, accumulates them into a single string variable, and prints the string.Here is a sample run of the program:
Please enter a letter: I Please enter a letter: l Please enter a letter: o Please enter a letter: v Please enter a letter: e Please enter a letter: P Please enter a letter: y Please enter a letter: t Please enter a letter: h Please enter a letter: o Please enter a letter: n Please enter a letter: ! Please enter a letter: ! Please enter a letter: ! Please enter a letter: ! The string is: IlovePython!!!!
Hint: As for running totals where we initialize the variable to 0, for variables that "accumulate" strings, we initialize the variable to the empty string (""). Here's a summary of the basic approach for the accummulating design pattern, broken down by the type of the accummulator variable:Running sums: Running products: Accumulating Strings: Accumulating Lists: Initialization: sum = 0 prod = 1 s = "" To be explained
after Chapter 5...Update Action: for ...
sum = sum + newValuefor ...
prod = prod * newValuefor ...
s = s + newValue
- Due Date: 24 February Reading: Chapter 3
Modify the book's factorial program to calculate the double factorial. The double factorial is similar to the factorial, except you multiply every other number. For example, 5!! = 5 * 3 * 1 and 8!! = 8 * 6 * 4 * 2. Formally, n!! = n*(n-2)*(n-4)*...*(1).
Hint: you only need to change the range statement.
- Due Date: 25 February Reading: Chapter 3
Implement the following piece of pseudocode as a complete program using turtle graphics:Repeat 45 times: Walk forward 100 steps Turn right 92 degreesYour output should look similar to:
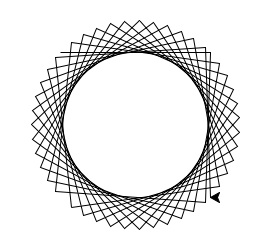
Hint: See Lab 3.
Note: Choose a name for your file that is not turtle.py. When executing the "import turtle" statement, the computer first looks in the folder where the file is saved for the turtle module and then in the libraries (and other places on the path). So, it thinks the module is itself, causing all kinds of errors. To avoid this, name your program something like "myTurtle.py" or "program8.py". - Due Date: 26 February Reading: Chapter 3
Modify the bouncing ball example from Lab 3 so that the ball bounces a little bit more each time. At the end, each bounce should go off the top of the screen.
Hint: the only change needed is to the height of the ball. How can you make the height get larger as time increases? - Due Date: 2 March Reading: Chapter 3
Using turtle graphics, draw a grid:
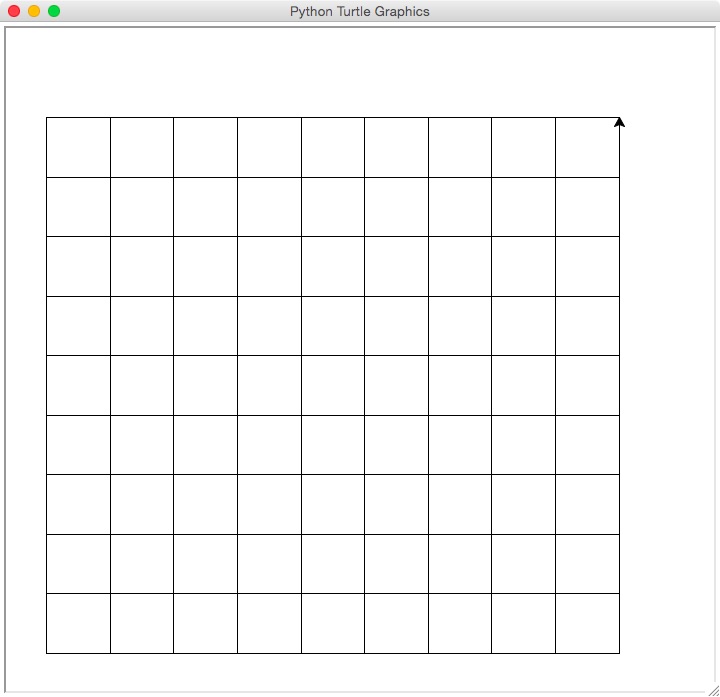
You may use any combination of turtle commands, but your image should have 9 by 9 grid shown above.
Hint: Resize the drawing canvas to give coordinates that are easier to use (see Lab 4). - Due Date: 3 March Reading: Chapter 3
Use turtle graphics to write your name to the screen, surrounded by a box or polygon. You may write your name in "cursive" by moving the turtle, or may use the write() command to have it printed to the graphics screen.
Hint: See Lab 4 for an example of the write() method for turtles. - Due Date: 5 March Reading: Chapter 3
Write a program that draws a 4 x 4 grid and places a turtle at a location specified by the user. When the user hits enter, move the turtle to the left side of the screen (but keep the same "height" as it moves). To make things easier, assume that the coordinates range from 0 to 3 for both the x and y values.For example, if the user enters the following at the Python shell:
Please enter coordinates: 2,1 Please hit the enter key to continue:
We draw the turtle at 2,1 (for reasons that will become apparent later, we're representing our turtle by the number "2"):
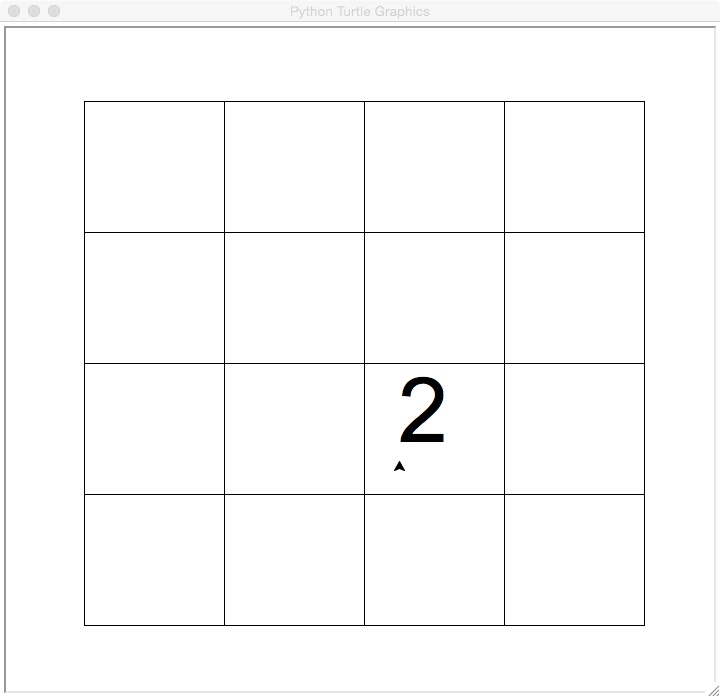
After the user hits the enter key, we have:

Hint: break the problem down into pieces:- First, draw the grid.
- Then ask the user for the coorinates.
- Move the turtle to those coordinates.
- Write to the screen.
- Then ask the user to hit the enter key.
- Next, move the turtle to the left.
- Write to the screen.
- Due Date: 9 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for a string and then prints it out in all upper case and then all lower case. Here is a sample run of the program:Please enter a string: Look behind, look here, look ahead You entered (shouting): LOOK BEHIND, LOOK HERE, LOOK AHEAD But better (whispering): look behind, look here, look ahead
- Due Date: 10 March Reading: Chapter 5
Modify the encode.py program from Lab 5 to use an offset entered by the user to encrypt the message. The program in the lab encrypts each character by shifting 1 place ahead in the alphabet. Your program should ask the user for the offset and encrypt their string by replacing each character by one that is offset places ahead in the alphabet.A sample of Caesar cipher disk (from en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caesar_cipher) with an offset of 13 (that is, every letter in plain text goes to one 13 letters to its right):
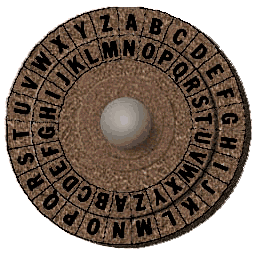
- Due Date: 11 March Reading: Chapter 5
Implement the following piece of pseudocode as a complete program:1. Prompt the user to enter a string and call it s. 2. Let l be the length of s. 3. For i from 0 upto l-1: 4. print s[0:i] 5. For i from 0 upto l-1: 6. print s[i:l] 5. Print a closing statementHere is a sample run of the program:Enter string: a man a plan a canal panama a a a m a ma a man a man a man a a man a a man a p a man a pl a man a pla a man a plan a man a plan a man a plan a a man a plan a a man a plan a c a man a plan a ca a man a plan a can a man a plan a cana a man a plan a canal a man a plan a canal a man a plan a canal p a man a plan a canal pa a man a plan a canal pan a man a plan a canal pana a man a plan a canal panam a man a plan a canal panama man a plan a canal panama man a plan a canal panama an a plan a canal panama n a plan a canal panama a plan a canal panama a plan a canal panama plan a canal panama plan a canal panama lan a canal panama an a canal panama n a canal panama a canal panama a canal panama canal panama canal panama anal panama nal panama al panama l panama panama panama anama nama ama ma a Thank you for using my program!
- Due Date: 12 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that prompts the user to enter 5 lines of text and then outputs the total number of characters that they entered.Here is a sample interaction:
Enter line: Sing me no song, read me no rhyme line character count is 33 Enter line: Don't waste my time, show me! line character count is 29 Enter line: Don't talk of June, don't talk of fall line character count is 38 Enter line: Don't talk at all! line character count is 18 Enter line: Show me! line character count is 8 The number of characters entered is: 126
- Due Date: 16 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that prompts the user to enter a list of names. Each person's name is separated from the next by a semi-colon (`;') and the names are entered lastName, firstName. Your program should then print out the names, one per line, with the first names first followed by the last names. Here is a sample interaction:Please enter your list of names: Falcon, Claudio; Ford, Eric; Owen, Megan; Rogers, Josh; St. John, Katherine You entered: Claudio Falcon Eric Ford Megan Owen Josh Rogers Katherine St. John Thank you for using my name organizer!
Hint: Do this problem in parts: first, split the list by person (what should the delimiter be?). Then, split each of person's name into first and last name (what should the delimiter be here?).
- Due Date: 17 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a text file, and then prints to the screen each of the lines in the file in upper case letters.For example, if your text file contained:
Input: first, get the input Process: then do the calculations Output: and last, print the results !!!
Then a sample run of your program would look like:
Please enter your file name: myFile.txt Your file in upper case letters is: INPUT: FIRST, GET THE INPUT PROCESS: THEN DO THE CALCULATIONS OUTPUT: AND LAST, PRINT THE RESULTS !!!
Hint: see the note about accumulators after Problem #9, Problem #19 and Lab 6. - Due Date: 18 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a text file, and then prints to the screen the lengths of each of the lines.For example, if your text file contained:
Sing me no song, read me no rhyme Don't waste my time, show me! Don't talk of June, don't talk of fall Don't talk at all! Show me!
Then a sample run of your program would look like:
Enter file name: song.txt Line character count is 33 Line character count is 29 Line character count is 38 Line character count is 18 Line character count is 8
Hint: what kind of value are you accumulating? See Problem #19 and Lab 6. - Due Date: 19 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a text file, and then prints to the screen the first character in each line.For example, if your text file contained:
Input: first, get the input Process: then do the calculations Output: and last, print the results !!!
Then a sample run of your program would look like:
Please enter your file name: myFile.txt The first letters of the lines in your file are: I P O !
- Due Date: 20 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a file. You may assume that every line of the contains a single floating point number. Your program should print out the sum of the numbers in the file.For example, if your file contained:
8.0 -2.5 100.0 6.5
Then a sample run of your program would look like:
Please enter your file name: nums.txt The sum of your numbers is 112.0.
Hint: see Problem #8 and Lab 6. - Due Date: 23 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a file. You may assume that every line of the contains floating point numbers separated by commas. Your program should print out the sum of the numbers in the file.For example, if your file contained:
-2.5, 2.0 8.0 100.0, 3.0, 5.1, 3.6 6.5
Then a sample run of your program would look like:
Please enter your file name: nums.txt The sum of your numbers is 125.7.
Hint: first sum up a single line, and then extend to an entire file. See Lab 6.
- Due Date: 24 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for a list of prices of items purchased and prints out each price and the total, formatted nicely. Here is a sample run of the program:Please enter the prices: 2.34, .99, 100, 81.05, 90 Your receipt: 2.34 0.99 100.00 81.05 90.00 ---------------- Total: 274.38Hint: use the format() statement discussed in Chapter 5. - Due Date: 25 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for a name of a file and then prints to the screen the number of characters and lines in the file. Hint: see Lab 6. - Due Date: 26 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of a file and a line length. Your program should then "wrap" all lines that are longer than line length, and print the result on the screen. For example, if the file contains:01234567890123456789012345 This line has more than 20 characters. This one has less And this one has lots, lots, lots, more than 20 characters!
and the user entered the length of 20, all lines longer than 20 would be wrapped to the next line:01234567890123456789 012345 This line has more t han 20 characters. This one has less And this one has lot s, lots, lots, more than 20 characters!
Hint: break the problem in to parts: first write a program that will print lines from a file to the screen (see Lab 6). Then modify your initial program to only print lines up to the length entered. And, to finish the program, then add in the code that prints lines that are longer than the length entered.- Due Date: 30 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for the name of file of addresses and a name of an output file. Your program should replace all occurrences of "NY" with "New York", all occurrences of "NJ" with "New Jersey", and all occurrences of "CT" with "Connecticut" and write the results to the output file. For example, if the input file contains:from wikipedia: NY-NJ-CT Tri-State Area The NY metropolitan area includes the most populous city in the United States (NY City); counties comprising Long Island and the Mid- and Lower Hudson Valley in the state of New York; the five largest cities in NJ and their vicinities; six of the seven largest cities in CT and their vicinities; and five counties in Northeast Pennsylvania.
Then the output file should be:from wikipedia: New York-New Jersey-Connecticut Tri-State Area The New York metropolitan area includes the most populous city in the United States (New York City); counties comprising Long Island and the Mid- and Lower Hudson Valley in the state of New York; the five largest cities in New Jersey and their vicinities; six of the seven largest cities in Connecticut and their vicinities; and five counties in Northeast Pennsylvania.
Hint: do each replacement one-by-one, that is, first get your program to replace all the "NY"s with "New York"s and then go on to the next states.- Due Date: 31 March Reading: Chapter 5
Write a program that asks the user for a file containing a list of items to be completed and a name for an output file. Your program should then write the list, with item numbers to the output file. For example, if the input file is:Finish my python homework. Buy milk. Do laundry. Update webpage.
Then the output file would be:1. Finish my python homework. 2. Buy milk. 3. Do laundry. 4. Update webpage.
- Due Date: 1 April Reading: Chapter 5
Modify the program from Lab 7 to include addresses in the file. The database has an additional attribute, address, and information can be included using the following format:insert into customer (first, last, address) values ('FirstName', 'LastName', 'Address')A sample input file is mayorsAddresses.txt.- Due Date: 2 April Reading: Chapter 5
Modify the program from Lab 7 to input a comma separated value (CSV) file and output a file where all fields are separated by tabs. That is, replace all commas in the file by TABs.
(Hint: See the list of string functions on p 140 of the textbook.)- Due Date: 13 April Reading: Chapter 5
(From Chapter 6, #1, Page 196) Write a program to print the lyrics of the song "Old MacDonald." Your program should print the lyrics for five different animals, similar to the example verse below.Old MacDonald had a farm, Ei-igh, Ee-igh, Oh! And on that farm he had a cow, Ee-igh, Ee-igh, Oh! Whith a moo, moo here and a moo, moo there. Here a moo, there a moo, everywhere a moo, moo. Old MacDonald had a farm, Ei-igh, Ee-igh, Oh!
Hint: use a function with two input parameters one for the animal and the other for the related sound.- Due Date: 14 April Reading: Chapter 6
Lab 8 focuses on top-down design; that is, beginning with an outline for the main() and filling in the function definitions. Fill in the missing function definitions for this program:from turtle import * def main(): myWin = turtle.Screen() #The graphics window tristan = turtle.Turtle() #Tristan will be our turtle for this program drawStem(tristan) #Draw a green stem for i in range(20): drawPetal(tristan,"blue") #Draws a blue petal for our flower drawPetal(tristan,"purple") #Draws a purple petal for our flower myWin.exitonclick() #Close the window when clicked
That is, write the functions drawStem() and drawPetal(). Include all functions, including the main() above in the file you submit. Sample output of the program:
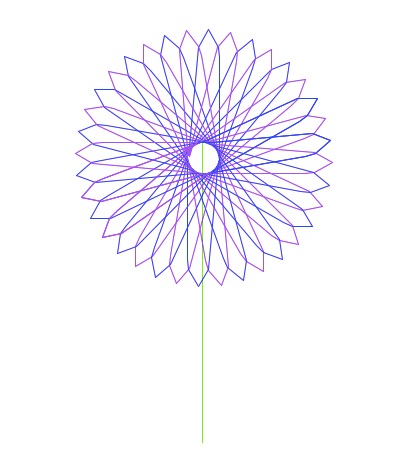
(Note: you can change the color that your turtle, using the function, color(). For example, if you turtle is called tess to change it's color in stringColor, write tess.color(stringColor).)
- Due Date: 15 April Reading: Chapter 6
Following Lab 8, fill in the missing function definitions for this program:def main(): welcome() #Prints "Welcome" to the screen age = userInput() #Ask the user for their age and return number entered y = calculate(age) #Using age, calculates year born displayResults(age,y) #Prints age and birth year main()(That is, write the functions welcome(), userInput(), calculate() and displayResults().) Submit a .py file containing all four functions you wrote, in addition to the main() function above.
- Due Date: 16 April Reading: Chapter 6
Write a function that takes as a parameter a list of strings and returns a list containing the lengths of each of the strings. That is, if the input parameter is ["apple pie", "brownies","chocolate","dulce de leche","eclairs"], your function should return [9, 8, 9, 14, 7]. The file you submit should include a main() function that demonstrates that your function works.Hint: This problem can be approached as an "accumulator", where we accumulate lists:
Running sums: Running products: Accumulating Strings: Accumulating Lists: Initialization: sum = 0 prod = 1 s = "" li = [] Update Action: for ...
sum = sum + newValuefor ...
prod = prod * newValuefor ...
s = s + newValuefor ...
li.append(newValue)
- Due Date: 17 April Reading: Chapter 6
Write a function that takes as a parameter a list of strings and returns a list containing the each string capitalized as a title. That is, if the input parameter is ["apple pie", "brownies","chocolate","dulce de leche","eclairs"], your function should return ["Apple Pie", "Brownies","Chocolate","Dulce De Leche","Eclairs"]. The file you submit should include a main() function that demonstrates that your function works.Hint: See problem above.
- Due Date: 20 April Reading: Chapter 6
Write a function that takes as a parameter a list of numbers and returns a list containing each number squared. That is, if the input parameter is [3,-1,0,2,10], your function should return [9,1,0,4,100]. The file you submit should include a main() function that demonstrates that your function works.- Due Date: 21 April Reading: Chapter 7
The program turtleString.py takes a string as input and uses that string to control what the turtle draws on the screen (inspired by code.org's graph paper programming). Currently, the program processes the following commands:- 'F': moves the turtle forward
- 'L': turns the turtle 90 degrees to the left
- 'R': turns the turtle 90 degrees to the right
- '^': lifts the pen
- 'v': lowers the pen
Modify this program to allow the user also to specify with the following symbols:
- 'B': moves the turtle backwards
- 'r': change the pen color to red
- 'g': change the pen color to green
- 'b': change the pen color to blue
Submit your modified program (including a comment at the top of the program with your name).
- Due Date: 22 April Reading: Chapter 7
Define a Python function named calculate_tax() which accepts one parameter, income, and returns the income tax. Income is taxed according to the following rule: the first $250,000 is taxed at 40% and any remaining income is taxed at 80%. For example, calculate_tax(100000) should return $100,000 * 0.40 = $40,000, while calculate_tax(300000) should return $250,000 * 0.40 + 50,000 * 0.80 = $140,000.In your file, you should include a main() that calls your function several times to demonstrate that it works.
- Due Date: 23 April Reading: Chapter 7
Write a function that takes as two parameters: the zone and the ticket type, and returns the Copenhagen Transit fare.- If the zone is 2 or smaller and the ticket type is "adult", the fare is 23.
- If the zone is 2 or smaller and the ticket type is "child", the fare is 11.5.
- If the zone is 3 and the ticket type is "adult", the fare is 34.5.
- If the zone is 3 or 4 and the ticket type is "child", the fare is 23.
- If the zone is 4 and the ticket type is "adult", the fare is 46.
- If the zone is greater than 4, return a negative number (since your calculator does not handle inputs that high).
You should include in the file a main() that calls your function several times to demonstrate that it works.
- Due Date: 24 April Reading: Chapter 7
Write a function that takes number between 1 and 7 as a parameter and prints out the corresponding number as a string. For example, if the parameter is 1, your function should print out one. If the parameter is 2, your function should print out two, etc.In your file, you should include a main() that allows the user to enter a number and calls your function to demonstrate that it works.
- Due Date: 27 April Reading: Chapter 8
The program lotsOfErrors.py has lots of errors. Fix the errors and sumbit the modified program.
Hint: see end of Lab 10.- Due Date: 29 April Reading: Chapter 8
Write a program that asks the user to enter a number between 0 and 1000, inclusive (that is, including the end points 0 and 1000). If they enter a number out of range, print a message that the number is out of range and prompt them again for a number between 0 and 1000, inclusive. When the user enters a number in range, print the number to the screen and end the program.- Due Date: 30 April Reading: Chapter 8
Write a program that reads in a text file, infile.txt, and prints out all the lines in the file to the screen until it encounters a line with fewer than 5 characters. Once it finds a short line (one with fewer than 4 characters), the program stops.
- Due Date: 4 May Reading: Chapter 8
Modify the program from Lab 10 that plays tic-tac-toe to check that the user chooses an empty square. Your program should ask the user for coordinates of where to play. While their choice of square if filled, you should continue to ask them until they choose an empty square. When the choose an empty square, the program continues as before.- Due Date: 5 May Reading: Chapter 8
Modify the program from Lab 11 to stop when the turtle wanders more than distance 100 from the starting point. The current program uses a definite loop to always move 500 steps. Change the program to use an indefinite loop that tests how far the turtle is from the origin. When that distance exceeds 100, your program should stop.
Hint: You only need to change the main() function of the exisiting program.- Due Date: 7 May Reading: Chapter 8
Modify the program from Lab 12 to ask the user for the number of chains (turtles) that your simulation should show. If the use user enters a negative number, your program should repeatedly ask the user for a positive number of turtles. Once they have entered the number of turtles, your program should then show that many chains (turtles) on the drawing screen.
Hint: You only need to change the main() function of the exisiting program.- Due Date: 11 May Reading: Chapter 13
Modify the program from Lab 13 that processes name files from the Social Security Admininstration. Your program should ask the user for a file name and a minimum name length and then print out the first name that is at least that length and then stop.For example, the input file NY.TXT starts out:
NYF1910Mary,1922 NYF1910Helen,1290 NYF1910Rose,990 NYF1910Anna,951 NYF1910Margaret,926 NYF1910Dorothy,897 NYF1910Ruth,712 NYF1910Lillian,648 NYF1910Florence,604 NYF1910Frances,589 NYF1910Elizabeth,579 NYF1910Mildred,562
Here a two sample runs of the program:Please enter the file name: NY.txt Please enter the minimum length: 5 The first name with length 5 or more is: Helen Thank you for using my name length searching program!
andPlease enter the file name: NY.txt Please enter the minimum length: 9 The first name with length 9 or more is: Elizabeth Thank you for using my name length searching program!
Hint: The program from the lab looks at every line of the file, but this program is a bit different in that it stops after it finds a long enough name. To do this, you need to change the loop to an indefinite loop (i.e. a while loop) or figure out how to break out of a definite loop (i.e. the for loop).
- Due Date: 12 May Reading: Chapter 13
Modify the selectionSort (from Chapter 13 of the book or Zelle's website) to sort lists of numbers backwards. For example, the list, [125,4,145,59,168,34,14,42], should be sorted as: [168,145,125,59,42,34,14,4]. In your submitted file, include a main() function that demonstrates that the sort algorithm works. Hint: See Lab 14. - Due Date: 30 March Reading: Chapter 5