import turtle
def main():
daniel = turtle.Turtle() #Set up a turtle named "daniel"
myWin = turtle.Screen() #The graphics window
#Draw a square
for i in range(4):
daniel.forward(100) #Move forward 10 steps
daniel.right(90) #Turn 90 degrees to the right
myWin.exitonclick() #Close the window when clicked
main()
Recall, our turtle, named daniel, moved forward 100 steps, made a 90 degree right
turn, and then repeated these actions for a total of 4 times. Let's modify it, so, that it
will draw an 8 sided polygon:
import turtle
def main():
numSides = 8 #Number of sides of the polygon
daniel = turtle.Turtle() #Set up a turtle named "daniel"
myWin = turtle.Screen() #The graphics window
#Draw a square
for i in range(numSides):
daniel.forward(100) #Move forward 10 steps
daniel.right(360/numSides) #Turn 90 degrees to the right
myWin.exitonclick() #Close the window when clicked
main()
To make it easier to modify, we stored the number of sides in just one place (the variable
named numSides) and use it in range statement in the for-loop as well as calculating
the amount needed to turn each time.
Run the program to make sure there's no errors. On the graphics window, you should see an octogon (8-sided) figure. How would you make an octogon like this:
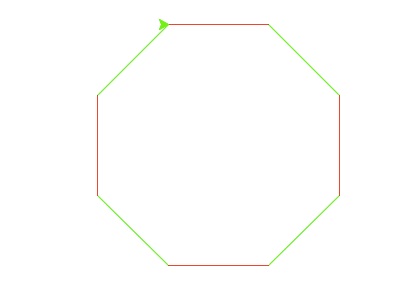
Notice that the edges change colors, the first, third, fifth, and seventh edges are red; while the second, fourth, sixth, and eighth edges are green. Since we start counting with 0, we have that the edges are red when the loop index variable i is 0,2,4,6. The edges are green when the loop index variable is 1,3,5,7.
To make the colors change, we need to test for when the loop index variable is even. A way to say that mathematically is i is even when i divided by 2 has no remainder. In python, we can write that as:
if i % 2 == 0:
daniel.color("red")
Let's add that to our program:
#Blinking turtle for introductory programming lab
import turtle
def main():
numSides = 8
daniel = turtle.Turtle() #Set up a turtle named "daniel"
myWin = turtle.Screen() #The graphics window
#Draw a square
for i in range(numSides):
if i % 2 == 0:
daniel.color("red")
daniel.forward(100) #Move forward 10 steps
daniel.right(360/numSides) #Turn 90 degrees to the right
myWin.exitonclick() #Close the window when clicked
main()
What does that do? How do we make the color green for when i is odd? Let's add in an
else to our if statement:
if i % 2 == 0: Turn daniel red else: Turn daniel greenPutting all the pieces together, we get:
#Blinking turtle for introductory programming lab
import turtle
def main():
numSides = 8
daniel = turtle.Turtle() #Set up a turtle named "daniel"
myWin = turtle.Screen() #The graphics window
#Draw a square
for i in range(numSides):
if i % 2 == 0:
daniel.color("red")
else:
daniel.color("green")
daniel.forward(100) #Move forward 10 steps
daniel.right(360/numSides) #Turn 90 degrees to the right
myWin.exitonclick() #Close the window when clicked
main()
Try the program to make sure that the colors change, depending on the value of i.
Next, change your program to make a 10-sided polygon (hint: you only need to change one line).